40 compare the movement of surface and deep currents
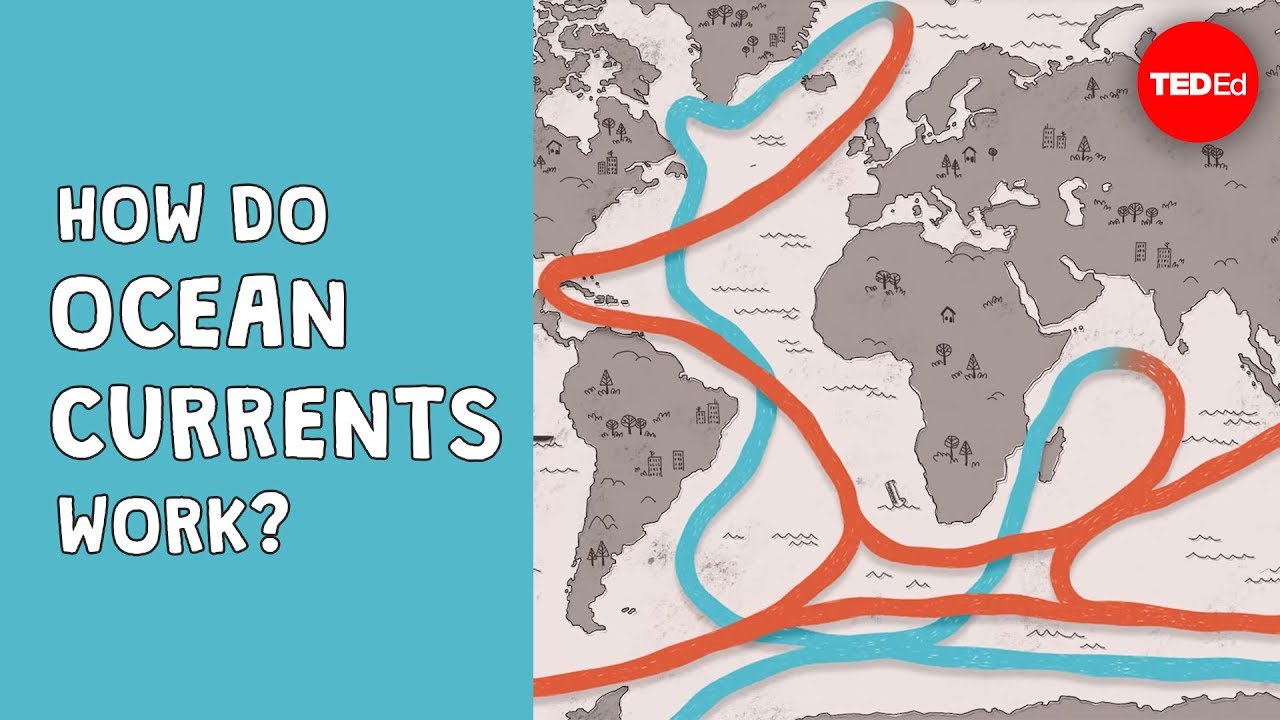
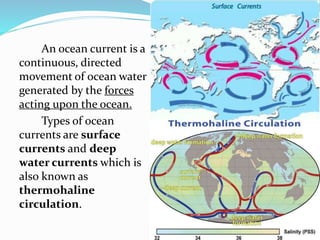
What causes ocean currents?: Ocean Exploration Facts: NOAA ... Surface wind-driven currents generate upwelling currents in conjunction with landforms, creating deepwater currents. Currents may also be caused by density differences in water masses due to temperature (thermo) and salinity (haline) variations via a process known as thermohaline circulation. These currents move water masses through the deep ... Deep Ocean Currents (Global Conveyor Belt) | HowStuffWorks Invisible to us terrestrial creatures, an underwater current circles the globe with a force 16 times as strong as all the world's rivers combined [source: NOAA: "Ocean"].This deep-water current is known as the global conveyor belt and is driven by density differences in the water.Water movements driven by differences in density are also known as thermohaline circulation because water density ...
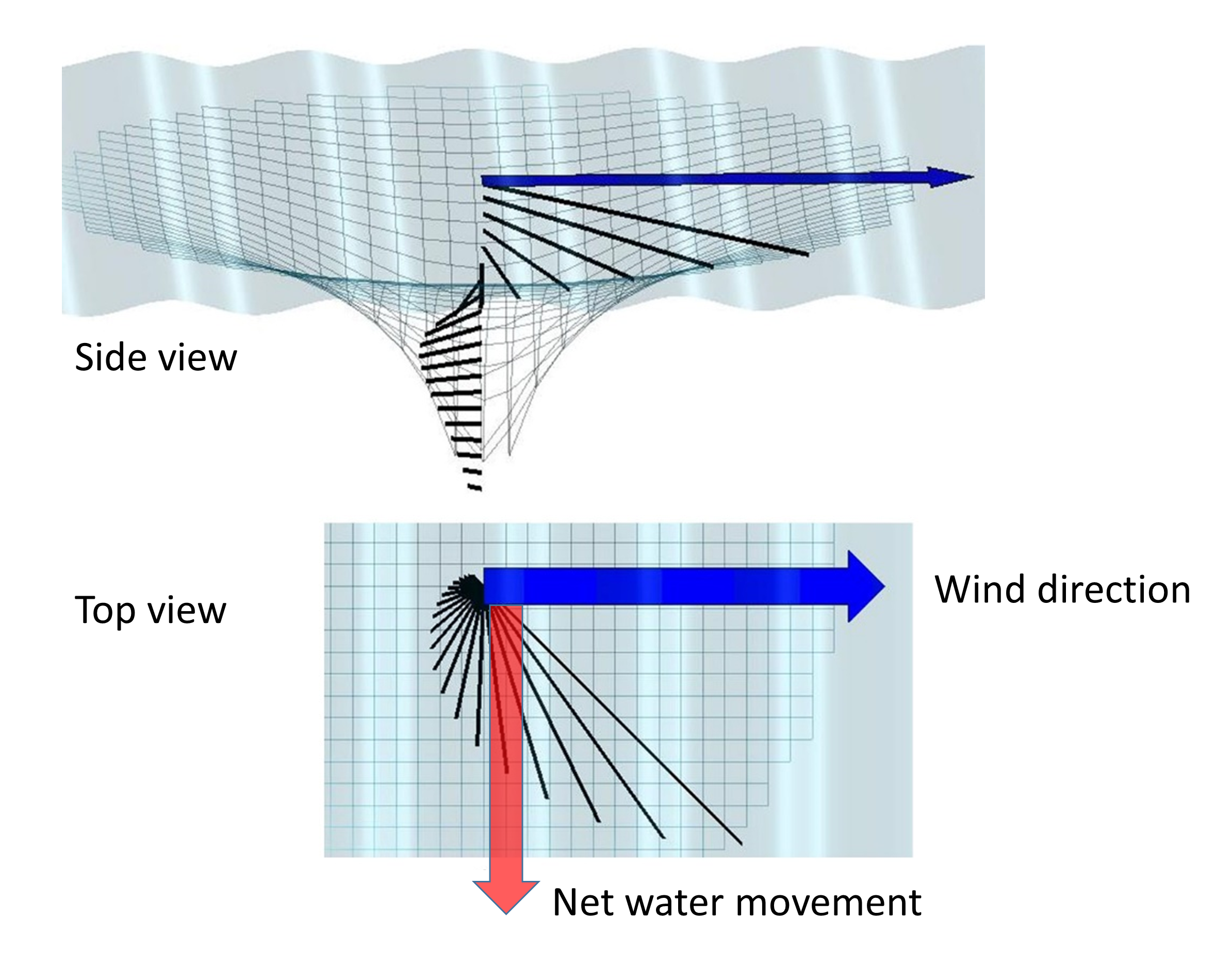
PDF Activity: Ocean Currents - Weebly There are: Surface currents are driven by wind and follow global atmospheric patterns. Cold surface currents move from the polar regions to the equatorial zones, and warm surface current move in the oppo site way. Deep currents are caused by the differences in water densities.
Compare the movement of surface and deep currents
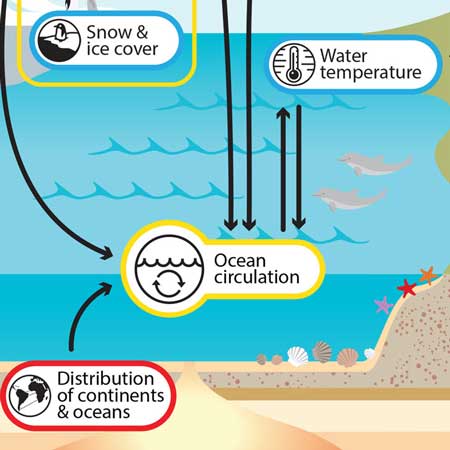
Ocean Currents and Climate - National Geographic Society worldwide movement of water (currents) in the ocean. ocean conveyor belt. Noun. system in which water moves between the cold depths and warm surface in oceans throughout the world. Also called thermohaline circulation. rip current. Noun. a strong flow of water running from the shore to the open ocean, sea, or lake. Ocean Currents and Their Global Impact - Lesson The movements of currents are also constrained by the shape of the ocean basins. When a current runs into a continent, it must turn aside. The complex interplay between wind, gravity, Coriolis Effect, and topography determines the location, size, shape, and direction of the surface current gyres. (For example, consider this North Atlantic gyre. PDF Ocean Surface Currents - 6th grade science which affect both surface and deep currents. These movements are essential to stirring the ocean, delivering oxygen to depth, distributing heat, and bringing nutrients to the surface. Stratification occurs when surface waters and deep waters are separated into layers by distinct differences in
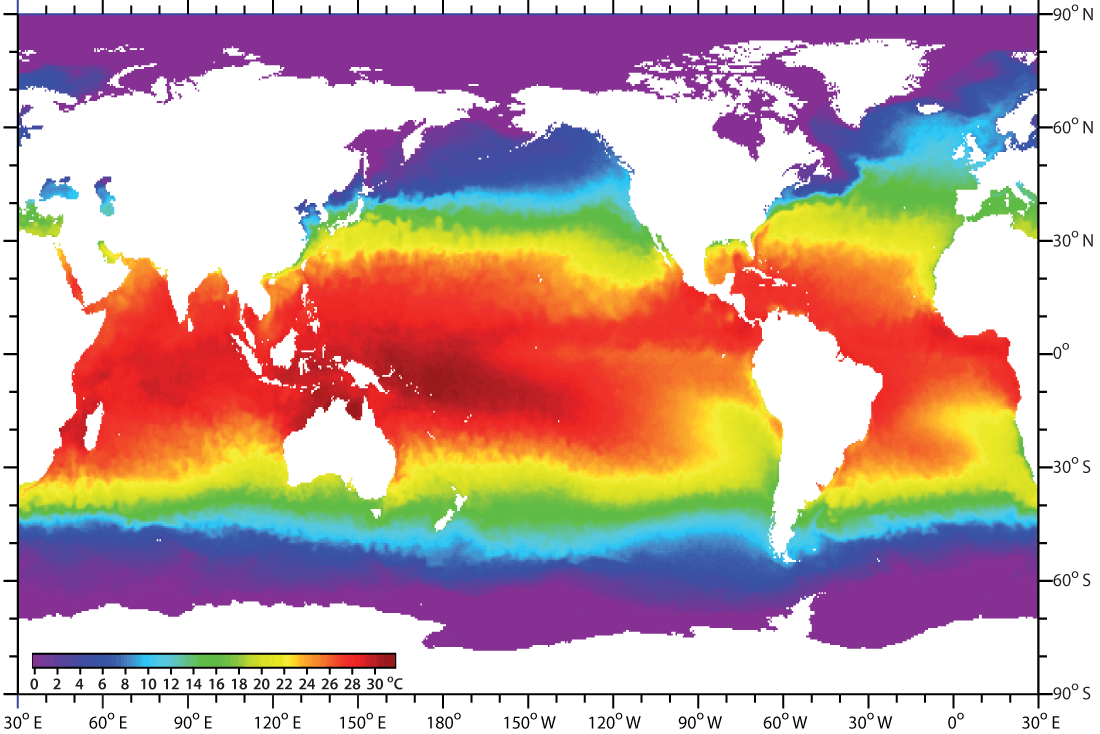
Compare the movement of surface and deep currents. 3 Differences between Sea Waves and Sea Currents ... Furthermore the difference between the two is seen from the location of the occurrence. Sea waves usually appear on the surface, causing sensations like waves. Meanwhile sea currents usually occur below sea level so that they are not visible from the surface. Compare and Contrast Deep ocean currents, and surface ... Surface currents are caused by wind blowing across the atlantic. (Affrects the top 30 feet) Surface currents Deep ocean currents Circulate tempature Move in a circular fomation called a Gyre. Colder water sinks and the warmer water rises to the top which helps bring oxygen down to animals at the bottom of the ocean. Show full text what is the difference between surface currents and deep ... Dec 20, 2021 · Deep currents are caused by differences in density at the top and bottom. More dense water takes up less space than less dense water. It has the same mass but less volume. What is the definition of surface currents? Surface currents are currents that are located in the upper 1,300 feet of the ocean, as opposed to deep in the ocean. Ocean currents | National Oceanic and Atmospheric ... Ocean water is on the move, affecting your climate, your local ecosystem, and the seafood that you eat. Ocean currents, abiotic features of the environment, are continuous and directed movements of ocean water. These currents are on the ocean's surface and in its depths, flowing both locally and globally.
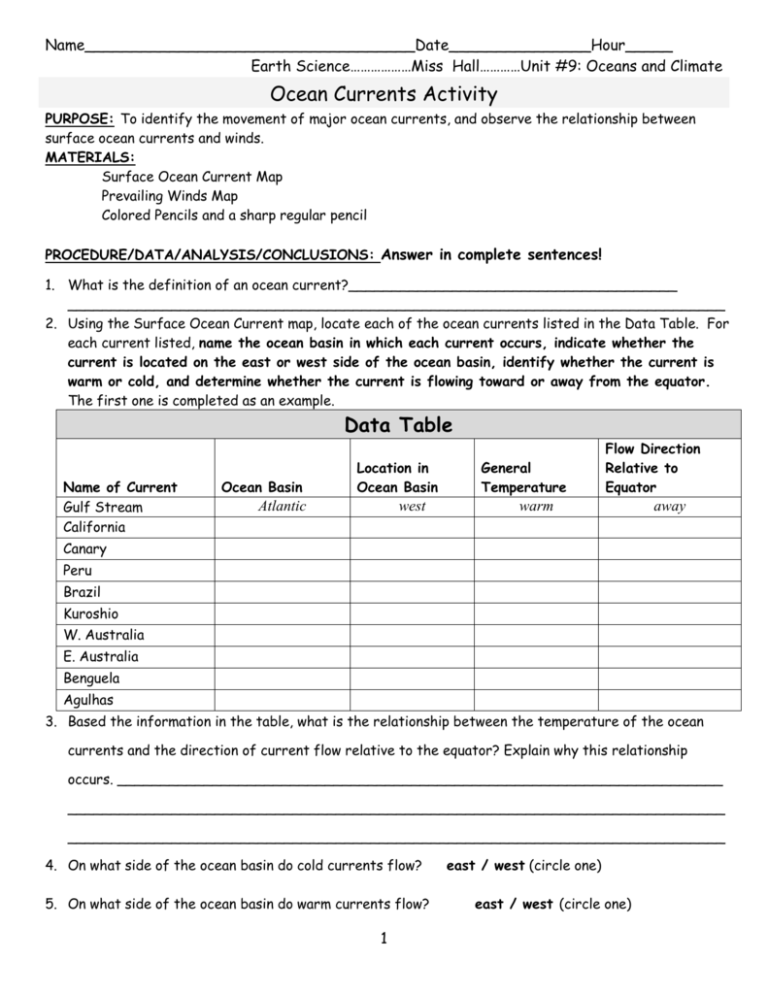
PDF Ocean Surface Currents Activity - Norwell High School Draw the movement of the water on your map, using red arrows. You may need to do this several times to correctly trace the movement of the water.!!!!! Part 4: Launch a Drifting Buoy! Cut a 2-cm (3/4-in.) piece from the end of one of the straws. This will be your drifting buoy. Carefully study the surface currents shown on your Surface Currents ... What is the difference between surface current and deep ... Best Answer. Copy. Surface currents depend on temperature and wind which is in the atmosphere but deep water currents do not as it occurs under water. Wiki User. ∙ 2010-03-15 15:52:28. This ... In one or two paragraphs, compare and contrast surface ... Surface currents refer to movement of the top layer of ocean water. Surface water flows in to replace the sinking water, which in turn becomes cold and salty enough to sink. examples of surface ocean currents are California Current (Cal) in the Pacific ocean basin and the Canary Current (Can) in the Atlantic ocean basin. Deep ocean currents Modeling Salinity and Deep Ocean Currents - NASA The surface ocean current brings new water to this region from the South Atlantic via the Gulf Stream and the water returns to the South Atlantic via the North Atlantic Deep Water current. The continual influx of warm water into the North Atlantic polar ocean keeps the regions around Iceland and southern Greenland mostly free of sea ice year-round.
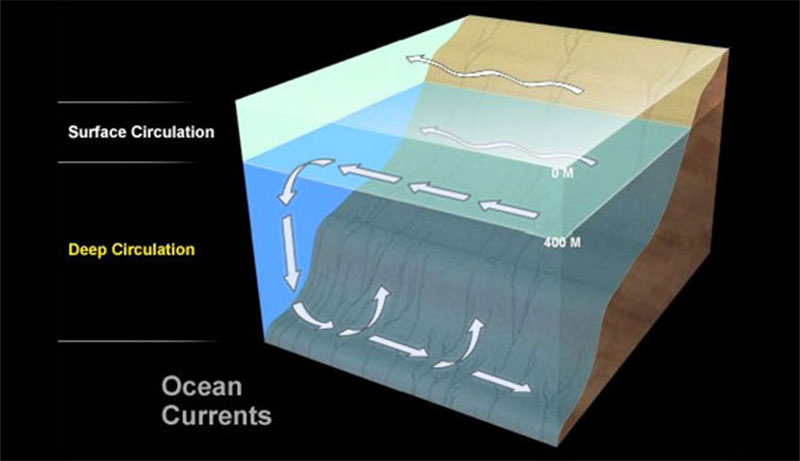
PDF CHAPTER SECTION 1 Currents - WPMU DEV Not all ocean currents are found at the surface. Movements of ocean water far below the surface are called deep currents. Unlike surface currents, deep currents are not controlled by wind. Deep current move-ments are controlled by water density. Density is the amount of matter in a given space or volume. The density of ocean water is affected by Horizontal and Vertical Ocean Currents - 1324 Words | 123 ... Ocean currents are horizontal or vertical movement of both surface and deep water throughout the world's oceans (Briney, n.d.). The primary generating forces are wind and differences in water density caused by variations in temperature and salinity. Currents generated by these forces are modified by factors such as the depth of the water ... Ocean Circulation: Surface Water and Deep Water | Earth ... The colors are a bit hard for me to see, but note that in the North Atlantic, a surface current flows north and a deep current flows south. This means that deep water forms in the North Atlantic. It's important to appreciate that any Figure drawn at this scale, the entire ocean, is approximate. Currents Flashcards - Quizlet upward movement of deeper, colder ocean water to the surface caused by wind thermohaline circulation movement of deep ocean water driven by differences in temperature, salinity, and density gyre large, rotating current loops caused by the Coriolis effect downwelling downward movement of surface ocean water caused by wind Sets with similar terms
What are 2 differences between surface currents and deep ... 18 Jan 2021 — What is the difference between density currents and surface currents? ... Deep ocean currents known as density currents are different from surface ...
What are the differences between surface currents and deep ... Surface currents are different from deep ocean currents because surface currents depend on the temperature, pressure, wind, and moon to determine them but deep water currents are too deep for any ...
Ocean currents- The movement of life ⋆ TheScientificRevelation surface currents only comprise 10% of ocean circulation. The rest 90% comes under deep ocean circulation. Surface currents are driven mainly by wind and wind is driven by Coriolis force. This cycle starts with temperature. In the equatorial region which receives the highest amount of sunlight and heat, air starts to get heated and rise.
Earth's Waters 4-4 Notes Flashcards - Quizlet Compare and contrast surface currents and deep currents. They are both are moving water that flows through oceans. Surface currents are towards the top of the ocean, can be warm or cold, and are controlled by winds. Deep currents are low, deep in the ocean, cold, and are controlled by density. How does upwelling effect marine life?
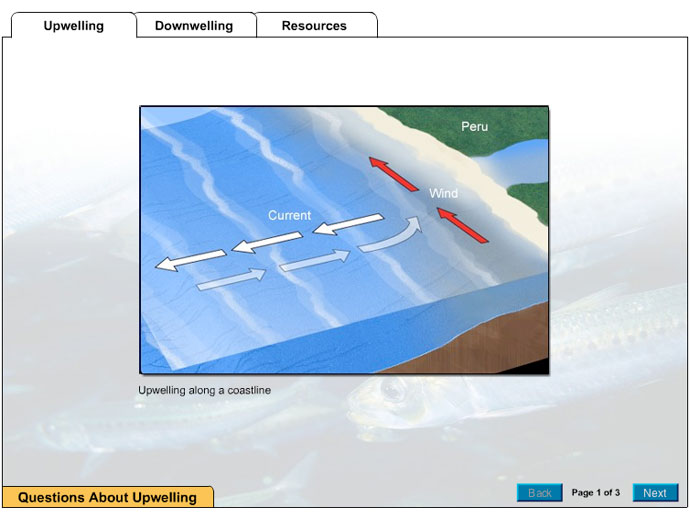
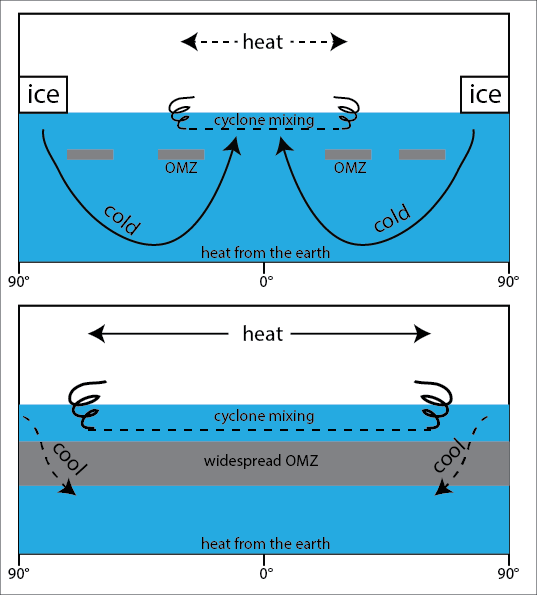
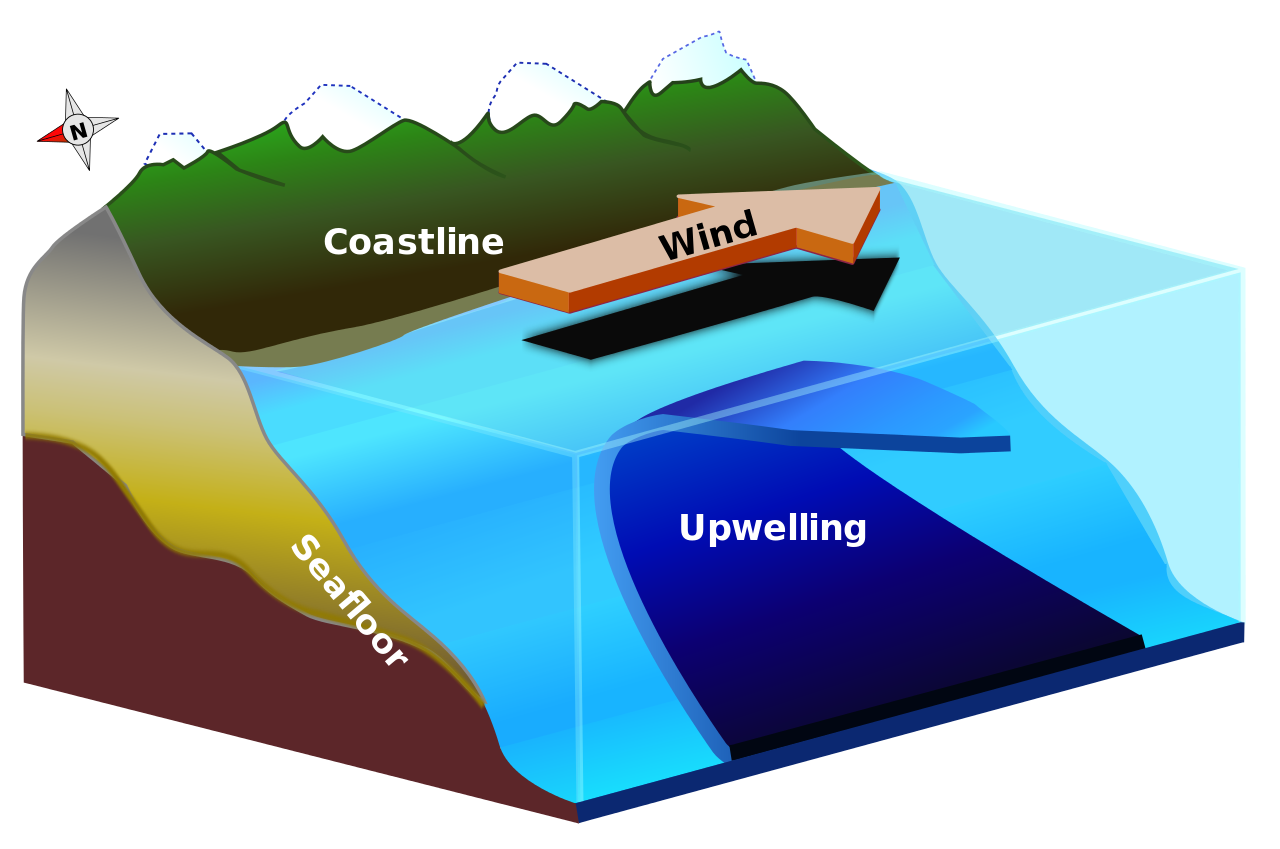
9.5: Currents, Upwelling and Downwelling - LibreTexts The movement of surface currents also plays a role in the vertical movements of deeper water, mixing the upper water column. Upwelling is the process that brings deeper water to the surface, and its major significance is that it brings nutrient-rich deep water to the nutrient-deprived surface, stimulating primary production (see section 7.3).
Two Types of Ocean Currents - Sciencing 23 Apr 2018 — Surface currents refer to movement of the top layer of ocean water – the upper 330 feet or so – primarily driven by wind. The large-scale ...
Understanding Surface Currents vs Deep Ocean Currents Surface currents are driven by global wind systems that are fueled by energy from the sun. These currents bring heat from the tropics to the polar regions; the Gulf Stream, for instance, brings warm water along the eastern coast of the US up to Northern Europe. Deep currents, also known as thermohaline circulation, result from differences in water density. These currents occur when cold, dense water at the poles sinks.
What is the difference between surface and deep currents 16 Dec 2021 — A. Surface currents move much more slowly, while deep currents travel quite quickly. B. Deep currents are driven by density differences, while ...
What is the difference between how surface currents and deep ... What is the movement of deep currents? — These deep-ocean currents are driven by differences in the water's density, which is controlled by ...
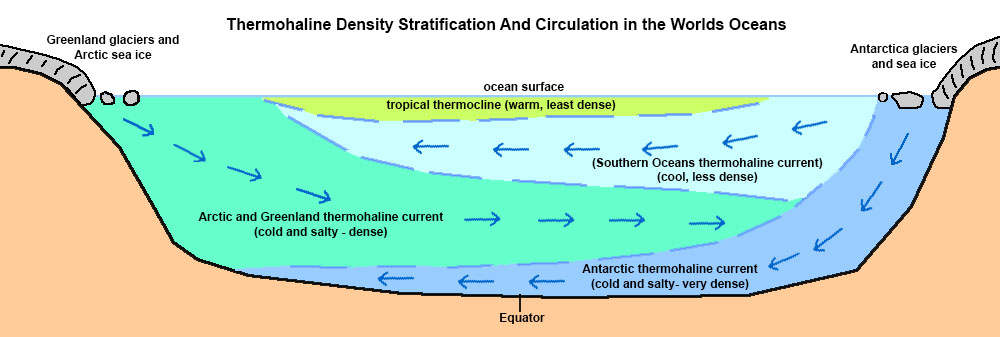
Thermohaline Circulation - Currents: NOAA's National Ocean ... Winds drive ocean currents in the upper 100 meters of the ocean's surface. However, ocean currents also flow thousands of meters below the surface. These deep-ocean currents are driven by differences in the water's density, which is controlled by temperature (thermo) and salinity (haline). This process is known as thermohaline circulation.
PDF CHAPTER SECTION 1 Currents Movements of ocean water far below the surface are calleddeep currents. Unlike surface currents, deep currents are not controlled by wind. Deep current move- ments are controlled by water density. Densityis the amount of matter in a given space or volume. The density of ocean water is affected by temperature and salinity.
PDF Ocean Currents and Sea Surface Temperature Part I: Obtain maps of sea surface temperature (SST) and ocean surface winds from the Live Access Server. 1. Click on the link for the Live Access Server. 2. Click on 'Choose Dataset' if it does not automatically appear. Select Oceans, Daily Sea Surface Temperature (GHRSST). 3. For region, have students select their own from the drop-down menu.
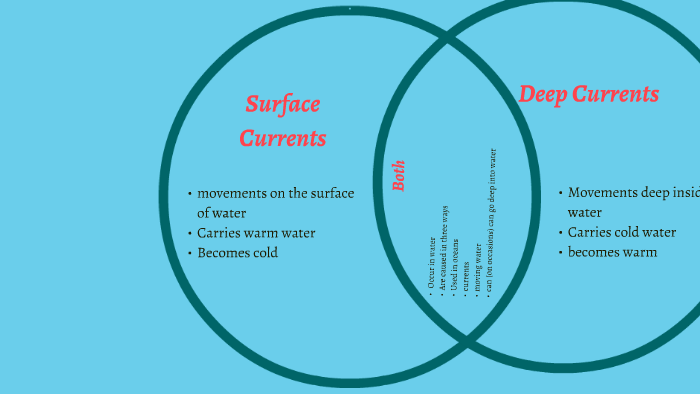
Surface currents vs. Deep currents by Cedric Wright Surface currents vs. Deep currents Occur in water Are caused in three ways Used in oceans currents moving water can (on occasions) can go deep into water Deep Currents Surface Currents Both Movements deep inside water Carries cold water becomes warm movements on the surface of
PDF Ocean Surface Currents - 6th grade science which affect both surface and deep currents. These movements are essential to stirring the ocean, delivering oxygen to depth, distributing heat, and bringing nutrients to the surface. Stratification occurs when surface waters and deep waters are separated into layers by distinct differences in
Ocean Currents and Their Global Impact - Lesson The movements of currents are also constrained by the shape of the ocean basins. When a current runs into a continent, it must turn aside. The complex interplay between wind, gravity, Coriolis Effect, and topography determines the location, size, shape, and direction of the surface current gyres. (For example, consider this North Atlantic gyre.
Ocean Currents and Climate - National Geographic Society worldwide movement of water (currents) in the ocean. ocean conveyor belt. Noun. system in which water moves between the cold depths and warm surface in oceans throughout the world. Also called thermohaline circulation. rip current. Noun. a strong flow of water running from the shore to the open ocean, sea, or lake.





















0 Response to "40 compare the movement of surface and deep currents"
Post a Comment